- DPC Latency Checker is a tiny and portable application that monitors computer activity and verifies if it is able to handle real-time streaming of audio and video data without interruptions.
- Latency is the amount of time it takes for a computer or application to respond to your request. The less time it takes the better. This is a test where you want to score low and there's a theoretical limit to how low you can go. Meaning the response was instant. Absolute zero is impossible on this test.
- LatencyMon checks if a system running Windows is suitable for processing real-time audio and other tasks. LatencyMon analyzes the possible causes of buffer underruns by measuring kernel timer latencies and reporting DPC and ISR execution times as well as hard pagefaults. The audio latency problem Windows is not a real-time operating system.
This is a RAM latency calculator. It takes the data rate (MHz) and cas latency (CL), then calculates the absolute latency for memory accesses in nanoseconds. Check latency from 12415 locations worldwide. ICMP PING Traceroute DNS Page load Http Get. Random probes on current map view. There are no results. There are no results.
Small and portable tool that checks system activity for latency issues, to find out if it's capable to handling audio and video real-time streaming without interruptions
DPC Latency Checker is a tiny and portable application that monitors computer activity and verifies if it is able to handle real-time streaming of audio and video data without interruptions. It does not include configuration parameters.
Since installation is not a prerequisite, you can drop the executable file anywhere on the hard disk and click it to run.
It is also possible to move DPC Latency Checker to a USB flash drive or similar storage unit, in order to use it on any machine with minimum effort.
An important aspect to keep in mind is that the Windows registry does not get new entries, and files are not left behind on the hard disk after program removal.
The interface of DPC Latency Checker is based on a standard window that contains a graph which tracks DPC latency. You can view the test interval, current latency, and absolute maximum value. Aside from stopping the monitoring process, you can reset the numerical values. There are no other options available through this tool. For example, you cannot ask DPC Latency Checker to record activity to file.
The simple application does not put a strain on system resources, as it requires a low amount of CPU and RAM to run properly. No error dialogs were shown in our tests, and the tool did not hang or crash. To conclude, DPC Latency Checker offers a straightforward solution to diagnosing computer latency issues with minimum effort.

Filed under
DPC Latency Checker was reviewed by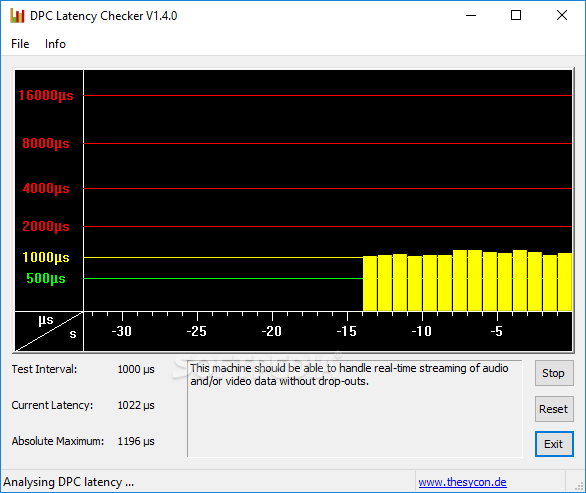 Elena Opris
Elena OprisDPC Latency Checker 1.4.0
add to watchlistsend us an update- runs on:
- Windows 10 32/64 bit
Windows 2003
Windows 8 32/64 bit
Windows 7 32/64 bit
Windows Vista 32/64 bit
Windows XP 32/64 bit
Windows 2K - file size:
- 299 KB
- filename:
- dpclat.exe
- main category:
- System
- developer:
- visit homepage
top alternatives FREE
top alternatives PAID
LatencyMonTarget audience | |||||||
|
Latest version: LatencyMon v 7.00
LatencyMon checks if a system running Windows is suitable for processing real-time audio and other tasks. LatencyMon analyzes the possible causes of buffer underruns by measuring kernel timer latencies and reporting DPC and ISR execution times as well as hard pagefaults. It will provide a comprehensible report and find the kernel modules and processes responsible for causing audio latencies which result in drop outs. It also provides the functionality of an ISR monitor, DPC monitor and a hard pagefault monitor.
LatencyMon will display the highest latencies of a kernel timer and report the highest execution times of ISR and DPC routines as well as hard pagefaults. In most cases it will also find the drivers and processes responsible for executing them. It will create a comprehensible report which also displays all sampled data in a detailed manner allowing you to perform in-depth analysis.
The audio latency problem
Windows is not a real-time operating system. All requests to the operating system are delivered on a best effort basis. There are no guarantees whatsoever that requests are delivered within a certain time frame, which are the characteristics of a real-time operating system. That is not a problem for most devices and tasks but this is bad news for audio applications (which are considered soft real-time) because they need to deliver data to the subsystem and the hardware in buffers several times per second. If one or more buffers miss their deadlines and are not delivered in time it has audible consequences which are recognized as dropouts, clicks and pops.
About DPCs and ISRs
The Windows thread dispatcher (also known as scheduler) which is part of the kernel executes threads based on a priority scheme. Threads with higher priority will be given a longer execution time (also known as quantum or time slice) than threads with a lower priority. However the kernel also knows other types of units of execution known as interrupt service routines (ISRs). Devices connected to the system may interrupt on a connected CPU and cause their interrupt service routines to execute. An interrupt can occur on the same processor that an audio program is running on. Any thread that was running on the processor on which an interrupt occurred will be temporarily halted regardless of its priority. The interrupt service routine (ISR) is executed and may schedule a DPC (Deferred Procedure Call) to offload an amount of work. The DPC will most likely run immediately on the same processor which means the audio application will halt until both the ISR and the DPC routines have finished execution. That is because ISRs and DPCs run at elevated IRQL which means they cannot become preempted by the thread dispatcher (scheduler). Therefore to guarantee responsiveness of the system, ISR and DPC routines should execute as fast as possible. Guidelines say that they should not spend more than 100 µs of execution time however this is often not reached due to hardware factors beyond the control of the driver developer. If execution time gets too high, the audio program may be unable to deliver audio buffers to the hardware in a timely manner.
Ping Checker
About hard pagefaults

Windows uses a concept of virtual memory which relies on the page translation system provided by the CPU. Whenever a memory address is requested which is not available in physical memory (not resident), an INT 14 will occur. The OS provided INT 14 handler will decide how to proceed next. If the page in which the address resides is known to Windows but not resident, Windows will read in the required page from the page file. That is known as a hard pagefault and can take a lot of time to complete. If the page can be read in from the hard disk cache, the price will be limited. However if it needs to physically read in the data from disk sectors this takes a lot of time. If an audio program hits a hard pagefault while it is playing it will almost certainly have audible consequences recognized as dropouts, clicks or pops.
Hard pagefaults are a very common but often overlooked cause of audio dropouts, clicks and pops. They especially occur often with audio software that uses a lot of memory such as samplers. Solutions for avoiding hard pagefaults are increasing the working set of the audio application, increasing the amount of RAM or disabling the pagefile altogether. Note that if you disable the pagefile, the system may run 'out of memory' because it does not have the pagefile available to swap memory to. Also the system will no longer create crash dump files in case of a system crash.
Latency Checker Tool
LatencyMon documentation and articles
· Introduction |
Note: this content is currently being updated.
Latency Checker
Copyright © 1997-2021 Resplendence Software Projects Sp. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy.Page generated on 5/19/2021 9:00:36 PM. Last updated on 9/16/2020 1:53:25 PM.